Before reading this post it is valuable for reading my previous post about FP tree. In that post I mentioned how to draw a FP tree using a given database table. If you already know how to draw a FP tree it's OK.
In that post we got the final output(Fp tree) as displays in Figure 1. And I think you remember that the Minimum support count is 3.
Let's find the Frequent Patterns(FPs) from FP tree.
The Items of the DB and there frequency of occurrences can be listed as
B:6
D:6
A:5
E:4
C:3
Note that the order of the list defined according to the priorities given in the Table2 of previous post. To observe the FPs we have to go through bottom to top, from C to B.
C
First need to find the conditional pattern base for C:3. If you wonder how 3 comes, it is due to frequency of occurrence of C. Now go to Figure 1 and check the Cs. There are 3 Cs and one occurrence for each. Now traverse bottom to top and get the branches which have Cs with the occurrence of C. For more clarification you can see Figure 2. We got 3 branches and they are
BDAE: 1 - The branch which surrounded in Blue.
B: 1 - The branch which surrounded in Red.
BAE: 1 - The branch which surrounded in Brown.
These branches regard as Conditional Pattern Base for C. You have to note three facts.
1. Even we traverse bottom to top we write the branches in top to bottom manner.
2. C is not there.
3. 1 came after each branch to represent the frequency of occurrence of C in each branch. You will more clear about this lately.
To ensure you correctly got all the occurrences of C in FP tree, add occurrences of C in each branch and compare with all the occurrences of C in FP tree; for this case 1+1+1 = 3 it is correct.
Then we have to find F-list from the Conditional Pattern Base of C. The list of items are B:3,D:1,A:2,E:2 but B:3 only eligible for sitting on the F-list due to fulfill the Minimum Support Count.So the F-list is
B:3
Now draw the Conditional FP tree for C. It is in Figure 3. When drawing the conditional FP tree you have to make sure to get Conditional Pattern Base as Ordered Items which mentioned in previous post Table 3. Now we can find C:3, BC:3 as identified FPs from tree.
If you answer a question paper the answer will be
Wait..Wait..this is not full answer.
Then we will find FPs by using item E.
E
Let's find Conditional Pattern Base for E:4. It depicts on Figure 4 and due to the previous explanation I think you already have the idea. If not ask as a comment.
BDA: 2 - Red line
BA:1 - Brown line
DA:1 - Blue line
And F-list will be
A:4
B:3
D:3
3 comes to B by 2 Bs coming from BDA: 2 and 1 B coming from BA:1. And 4 As and 3 Ds also according to that manner. Why A appears before the B in F-list even B appears before previously? That have a reason. We got a list from this Conditional Pattern Base as B:3, D:3, A:4. But in F-list they should appear according to their frequency of occurrences in Conditional Pattern Base. So A coming to front and others going to back. Then it is easy to use for creating conditional FP tree for E.
Figure 5 displays Conditional FP tree for E according to the same method described in previous post. Make sure to use Conditional Pattern Base as Ordered Items.
For a moment forget the FP tree and conditional FP tree for E put on to your mind. So think we only have this FP tree and need to find FPs from this.
Items in this FP tree are
A:4
B:3
D:3
Let's go bottom to top.
DE
From where DE comes ? Even we deleted FP tree it remains in the Recycled Bin. :) We are going to identify FPs for DE. Because of we use conditional FP tree for E, E comes to back.
Conditional pattern base for DE:3
A:1, AB:2
F-list: A:3
Conditional FP-tree for DE : Figure 6
Frequent patterns
DE:3, ADE:3
I think you don't need explanation. Then we are going to find FPs by using BE.
BE
Conditional pattern base for BE:3
A:3
F-list: A:3
Conditional FP-tree for DE : Figure 6
Frequent patterns
BE:3, ABE:3
Then move to AE.
AE
Conditional pattern base for AE:4
NULL
Conditional FP-tree for DE
NULL
Frequent patterns
AE:4
We find all FPs of conditional FP tree for E. Next step is remind the previous or main tree. And before leave E we can write E:4 also as a FP. Let's move to A.
A
Conditional pattern base for A:5
BD: 3; B:1; D:1
F-list: B:4, D:4
Conditional FP-tree for A : Figure 7
Then we will go on the conditional FP tree for A as like as previous trip.
AD
Conditional pattern base for AD:4
B:3
F-list :B:3
Conditional FP-tree for AD : Figure 3
Frequent patterns
AD:4, ABD:3
AB
Conditional pattern base for AB:4
NULL
Frequent patterns
AB:4
And also can get A:5 as a FP.
D
Conditional pattern base for D:6
B: 4
F-list : B:4
Conditional FP-tree for D : Figure 8
Frequent patterns
D:6, BD:4
Then last item, B.
B
Conditional pattern base for B:6
NULL
Conditional FP-tree for B
NULL
Frequent patterns
B:6
Hurray! We finish all items and this is time to collect all bins in to a single bin. The identified frequent itemsets from the Database (Table 1 in Previous post) with minimum support as 30% are C:3, BC:3, DE:3, ADE:3 , BE:3, ABE:3, AE:4, E:4, AD:4, ABD:3, AB:4, A:5, D:6, BD:4, B:6.
I'm sure you don't need any support for creating full answer. Please leave your comments below if this is valuable to you.
 |
| Figure 1 |
Let's find the Frequent Patterns(FPs) from FP tree.
The Items of the DB and there frequency of occurrences can be listed as
B:6
D:6
A:5
E:4
C:3
Note that the order of the list defined according to the priorities given in the Table2 of previous post. To observe the FPs we have to go through bottom to top, from C to B.
C
 |
| Figure 2 |
BDAE: 1 - The branch which surrounded in Blue.
B: 1 - The branch which surrounded in Red.
BAE: 1 - The branch which surrounded in Brown.
These branches regard as Conditional Pattern Base for C. You have to note three facts.
1. Even we traverse bottom to top we write the branches in top to bottom manner.
2. C is not there.
3. 1 came after each branch to represent the frequency of occurrence of C in each branch. You will more clear about this lately.
To ensure you correctly got all the occurrences of C in FP tree, add occurrences of C in each branch and compare with all the occurrences of C in FP tree; for this case 1+1+1 = 3 it is correct.
Then we have to find F-list from the Conditional Pattern Base of C. The list of items are B:3,D:1,A:2,E:2 but B:3 only eligible for sitting on the F-list due to fulfill the Minimum Support Count.So the F-list is
B:3
Now draw the Conditional FP tree for C. It is in Figure 3. When drawing the conditional FP tree you have to make sure to get Conditional Pattern Base as Ordered Items which mentioned in previous post Table 3. Now we can find C:3, BC:3 as identified FPs from tree.
 |
| Figure 3 |
If you answer a question paper the answer will be
Conditional pattern base for C:3
BDAE: 1; B: 1; BAE: 1
F-list: B:3
Conditional FP-tree for C (Draw Figure 3.)
Frequent patterns
C:3, BC:3
Wait..Wait..this is not full answer.
Then we will find FPs by using item E.
E
Let's find Conditional Pattern Base for E:4. It depicts on Figure 4 and due to the previous explanation I think you already have the idea. If not ask as a comment.
 |
| Figure 4 |
BA:1 - Brown line
DA:1 - Blue line
And F-list will be
A:4
B:3
D:3
3 comes to B by 2 Bs coming from BDA: 2 and 1 B coming from BA:1. And 4 As and 3 Ds also according to that manner. Why A appears before the B in F-list even B appears before previously? That have a reason. We got a list from this Conditional Pattern Base as B:3, D:3, A:4. But in F-list they should appear according to their frequency of occurrences in Conditional Pattern Base. So A coming to front and others going to back. Then it is easy to use for creating conditional FP tree for E.
 |
| Figure 5 |
For a moment forget the FP tree and conditional FP tree for E put on to your mind. So think we only have this FP tree and need to find FPs from this.
Items in this FP tree are
A:4
B:3
D:3
Let's go bottom to top.
DE
From where DE comes ? Even we deleted FP tree it remains in the Recycled Bin. :) We are going to identify FPs for DE. Because of we use conditional FP tree for E, E comes to back.
 |
| Figure 6 |
A:1, AB:2
F-list: A:3
Conditional FP-tree for DE : Figure 6
Frequent patterns
DE:3, ADE:3
I think you don't need explanation. Then we are going to find FPs by using BE.
BE
Conditional pattern base for BE:3
A:3
F-list: A:3
Conditional FP-tree for DE : Figure 6
Frequent patterns
BE:3, ABE:3
Then move to AE.
AE
Conditional pattern base for AE:4
NULL
Conditional FP-tree for DE
NULL
Frequent patterns
AE:4
We find all FPs of conditional FP tree for E. Next step is remind the previous or main tree. And before leave E we can write E:4 also as a FP. Let's move to A.
A
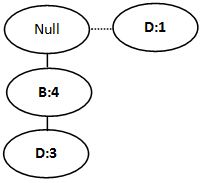 |
| Figure 7 |
BD: 3; B:1; D:1
F-list: B:4, D:4
Conditional FP-tree for A : Figure 7
Then we will go on the conditional FP tree for A as like as previous trip.
AD
Conditional pattern base for AD:4
B:3
F-list :B:3
Conditional FP-tree for AD : Figure 3
Frequent patterns
AD:4, ABD:3
AB
Conditional pattern base for AB:4
NULL
Frequent patterns
AB:4
And also can get A:5 as a FP.
 |
| Figure 8 |
Conditional pattern base for D:6
B: 4
F-list : B:4
Conditional FP-tree for D : Figure 8
Frequent patterns
D:6, BD:4
Then last item, B.
B
Conditional pattern base for B:6
NULL
Conditional FP-tree for B
NULL
Frequent patterns
B:6
Hurray! We finish all items and this is time to collect all bins in to a single bin. The identified frequent itemsets from the Database (Table 1 in Previous post) with minimum support as 30% are C:3, BC:3, DE:3, ADE:3 , BE:3, ABE:3, AE:4, E:4, AD:4, ABD:3, AB:4, A:5, D:6, BD:4, B:6.
I'm sure you don't need any support for creating full answer. Please leave your comments below if this is valuable to you.
gooooooood...
ReplyDeleteThank you!
Deletethat's helpful
ReplyDeleteNice to hear it. Thanxx!
DeleteThat's Really Helpful,Keep up the good work
ReplyDeleteThank you Rajesh.. Comments like this encourage me to Blogging...
DeleteYou did a great job! It's easy to realize FP-growth by this example. Thank you for your effort
ReplyDeleteYou are Welcome!
DeleteI echo the thanks of others! I realise I am a bit late- but with the help of this blog I was able to get an implementation of this working in Java!
DeleteWhy Conditional pattern base for AE is NULL ? It should be B : 3 and D : 3.
ReplyDeleteIt should not, because it's like you "delete" B and D after mining their FPs. So your conditional pattern base is the prefix of AE and only the root tree (NULL) is left out. Consequently FP conditional tree for AE is built with AE prefix and so it's NULL too.
DeleteIn my opinion, we "mine" the new Conditional FP-Tree (in figure 5) for the information of AE, not the original FP-Tree. Therefore, there is no "BD" prefix for the A node.
DeleteHi, thanks for this great post! Congratulations!
ReplyDeleteOnly one question about it: why do you find AD and AB instead of DA and BA? If you were mining A, then A comes to back just like E, isn't it?
Thank you for this great post, I have to do a report about FP-Growth and you have helped me a lot when trying to understand the algorithm.
ReplyDeleteThen we have to find F-list from the Conditional Pattern Base of C. The list of items are B:3,D:1,A:2,E:2 but B:3 only eligible for sitting on the F-list due to fulfill the Minimum Support Count.So the F-list is
ReplyDeleteB:3
why we didn't calculated the occurrence of other branch means right side branch
D will be 3, A will be 3, E will be 3
so do i, i can't understand this part
DeleteThank you so much!
ReplyDeleteVery good work...
ReplyDeleteA very good article....:)
ReplyDelete"From where DE comes ?" Sorry, this step I didn't understand. Dumb me!
ReplyDeleteplease help me with this sum.i got stuck in finding frequent pattern for C.
ReplyDeleteTid items
1 a,b
2 b,c,d
3 a,c,d,e
4 a,d,e
5 a,b,c
6 a,b,c,d
7 a
8 a,b,c
9 a,b,d
10 b,c,e
minimum support count=3
From where DE comes ?" Sorry, this step I didn't understand. Please help
ReplyDeleteSame here.. Could not understand how DE came?
Deletethank for your explanation. it help me a lot to finish my final exam.
ReplyDeleteI am really impressed with your writing skills as well as with the layout on your blog.
ReplyDeleteIs this a paid theme or did you customize it yourself?
Either way keep up the excellent quality writing, it's rare to see a nice blog like this one today.
Feel free to visit my web blog ... Read More
Thanks. You facilitate grasping how it works.
ReplyDeleteHi,
ReplyDeleteExcellent post explaining how to calculate the tree and everything. I just have a doubt (Maybe a silly one).
What is the real meaning in human readable words of the resulting pattern? For example C:3, BC:3, DE:3.... means that we found exactly what? If they are products on a grocery list, C:3 would mean...?
Thanks again for your post.
Regarding human readable context.
ReplyDeleteConsider this image http://hareenlaks.blogspot.com/2011/06/fp-tree-example-how-to-identify.html
each transaction/line is a customer's transaction in super market store. and each space separated character like A,B,C are item in customer's cart.
gandu sala. kuch bhi de raha hai.
ReplyDeleteyou're right bro! he has just copied all stuffs from some page and published.
Deleteyou assholes. you don't know shit and you're here to judge his talent. f'cking losers!!! get a life mofo
DeleteThank you so much
ReplyDeleteI have a question
ReplyDeletewhen we construct a conditional fp tree: do we realy do that or we just get a projection from the original fp tree ?
I ask this question becoze if we every time construcr a conditional fp tree, this will cost so much in memory and time !
This is really so good!
ReplyDeleteif you have an php implementation i will be grateful
ReplyDeletes6930064@hotmail.com
Nicely explained!... Thanks :)
ReplyDeleteIt helped me... Thank you. :)
ReplyDeletepoor grammar...
ReplyDeleteWhy A:4 while calculating conditional pattern of E......
ReplyDeleteSame doubt🙈
DeleteSince from what I know..we also check whether both the patterns belong to the same branch in order to perform computation between the two.accirding to that..A cannot be 4
Deletei still cant get it :(
ReplyDeleteim going to die bcs fp growth huhuhu
So, there's no confidence at last? How do we know if the frequent pattern is trustable? Or is it already trustable without calculating the confidence?
ReplyDeleteawesome explanation thank you so much
ReplyDeleteyou saved my time!
This comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteBest explanation..thanks sir it helped me a lot n saved my time
ReplyDeleteAwesome work man
ReplyDeletewhy youhave taken conditional base pattern for AE equal to NULL. i think it should be B 1, BDA 2,D 1
ReplyDeleteAre you sure that the conditional FP tree that is redrawn is completely new? As in the items in different branches are kind of merged in your example. In Alex Berson: Data Warehousing, it doesn't seem like they have done it that way.
ReplyDeleteOther than that the explanation is really crystal clear.
Please cite your references so that we can get to know more about it.
Thank you!
This comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteHow to find conditional pattern base for DE. PLEASE HELP...
ReplyDeletecanada goose outlet
ReplyDeletechicago bears jerseys
off white shoes
moncler outlet
nike sale
off white nike
ralph lauren polo
canada goose jackets
asics shoes
pandora charms
Worst explanation
ReplyDeleteManan, why are you destroying the hard work of a person just for your fun? :(
DeleteOMG, how bad can an article be!!
ReplyDeleteJust stop!!!
Yeah , totally agreed
DeleteHi. Why is BDA: 2 for finding the conditional base for E4
ReplyDeleteAwesome and interesting article. Great things you've always shared with us. Thanks. Just continue composing this kind of post. Tree Services
ReplyDeleteVery Nice!
ReplyDeleteyeezy boost 350
ReplyDeletekyrie 7
golden goose outlet
moncler
nike dunks
hermes birkin
kyrie 5 shoes
yeezy shoes
kyrie 5
kyrie 6
best site v9h29q5z03 replica louis vuitton handbags replica bags by joy replica bags ru have a peek at this site v9p24x0u39 replica bags dubai replica goyard bags try this out q2x98h9f31 replica bags gucci
ReplyDeletevfr9513hnd
ReplyDeletegolden goose outlet
golden goose outlet
golden goose outlet
golden goose outlet
golden goose outlet
golden goose outlet
golden goose outlet
golden goose outlet
golden goose outlet
golden goose outlet